High Dust Load PTFE
Both glass fiber and PTFE can be used for HEPA or ULPA class cleanroom filters. The main difference between these two materials is their filtration mechanisms. In glass fiber media, particle capture occurs within the depth of the filter, whereas in PTFE media, filtration happens primarily on the surface. This surface filtration gives PTFE media several advantages, including high filtration efficiency, lower pressure drop, and improved energy efficiency. However, this same mechanism typically results in lower dust holding capacity compared to glass fiber media.
Designed to capture and retain large volumes of dust without frequent replacement.
Designed to capture and retain large volumes of dust without frequent replacement.
At LyneYi, we leverage advanced filtration technologies by combining multiple filter layers with PTFE membranes to develop a high dust-load PTFE solution. Our engineered media achieves up to nine times the dust holding capacity of conventional PTFE, while maintaining a resistance that is only 50% of traditional glass fiber media.
Suitable for high humidity environment
PTFE filter media is inherently hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. As a result, it can be used in high-humidity environments without risk of damage to the PTFE-based filter.
Additionally, it has been tested with a range of disinfectants commonly used in biopharmaceutical, food & beverage processing, and healthcare industries. The hydrophobic nature of PTFE makes it an ideal choice for cleanroom environments with higher humidity.
Additionally, it has been tested with a range of disinfectants commonly used in biopharmaceutical, food & beverage processing, and healthcare industries. The hydrophobic nature of PTFE makes it an ideal choice for cleanroom environments with higher humidity.
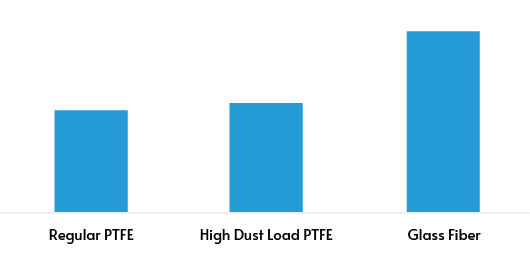
Filter Media Pressure Drop Comparison
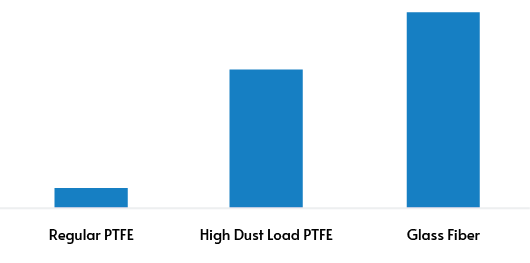
Filter Media Dust Loading Capacity Comparison
Bio-decontamination and disinfection Test
UV and Ozone Exposure Compatibility Test
| Filter Model | UV Radiation | Ozon Concentration (ppb) | Exposure Time | Outlook | Test Aerosol | Face Velocity (m/s) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H14-610x610x93mm | 254nm | 700 -1000 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9989 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 254nm | 700 -1000 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9987 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 254nm | 700 -1000 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9991 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 254nm | 700 -1000 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9987 |
Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP) Exposure Compatibility Test
| Filter Model | Relative Humidity (%) | VHP Concentration (ppb) | Exposure Time | Outlook | Test Aerosol | Face Velocity (m/s) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H14-610x610x93mm | 40±15% | 250 | 60 mins | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9991 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 40±15% | 250 | 60 mins | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9989 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 40±15% | 250 | 60 mins | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9985 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 40±15% | 250 | 60 mins | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9988 |
Alcohol/ Isopropanol Exposure Compatibility Test
| Filter Model | Relative Humidity (%) | Concentration | Exposure Time | Outlook | Test Aerosol | Face Velocity (m/s) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H14-610x610x93mm | 50±10% | 75-80 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9986 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 50±10% | 75-80 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9991 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 50±10% | 75-80 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9988 |
| H14-610x610x93mm | 50±10% | 75-80 | 24 hours | ok | PAO | 1.00 | 99.9989 |
Want to test our technology?
Experience the power of our nanofiber technology for yourself.
Request a free sample today and see how our materials can enhance your product’s performance.
